The calculation of a Joule is a complicated electrical principle that defines the amount of electrical work being transferred (or work done). The simple equation is Volts x Amps (Watts) x On-time = Joules or the work required to produce one watt of power for one second, or one "watt second".
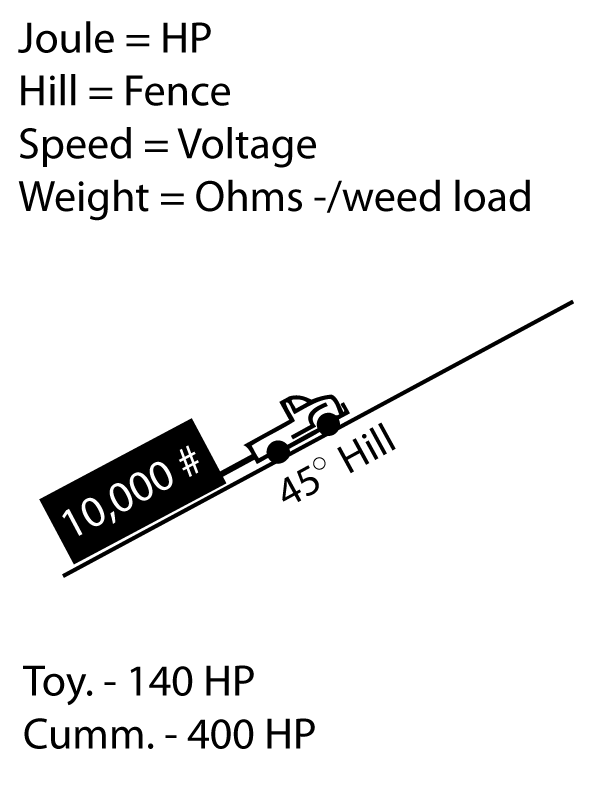
The Joule rating has become a standard in defining the power that can be transferred to a fence conductor from an electric fence charger or energizer, as they are sometimes called. This energy transfer rating was defined in the late 1800’s but was not applied to electric fence chargers until the introduction of the Low Impedance style chargers originally referred to as non-shortable energizers. This style of fence charger has become the standard in today’s electric fence market and delivers a high voltage pulse with an on-time duration of milliseconds. They were developed to overcome shorting out on plants and also to eliminate the danger of injury from electric current when the pulse on-time is too long. The brief, high energy pulse cannot generate heat which is the damaging element of electric shock.
The Joule rating has become a standard in defining the power that can be transferred to a fence conductor from an electric fence charger or energizer, as they are sometimes called. This energy transfer rating was defined in the late 1800’s but was not applied to electric fence chargers until the introduction of the Low Impedance style chargers originally referred to as non-shortable energizers. This style of fence charger has become the standard in today’s electric fence market and delivers a high voltage pulse with an on-time duration of milliseconds. They were developed to overcome shorting out on plants and also to eliminate the danger of injury from electric current when the pulse on-time is too long. The brief, high energy pulse cannot generate heat which is the damaging element of electric shock.
See our line of fence energizers and grounding hardware.